The mobile world is constantly changing. When your business observes a need to have a mobile app to run across major platforms and devices, you often face the dilemma that which platform to deploy – Native or cross-platform?
If you favor one specific platform for your app to live in, the traditional “Build Apps Natively” approach should work perfectly for you. However, if you consider all three major platforms for your app development, then you have to build each app exclusively for iOS, Android, or Windows individually, so you need to have multiple codebases and have to hire a large team of developers for each platform.
It usually delays the completion and subsequently, makes the innovation of new features sluggish since focus eventually shifts on platform-specific issues rather than on developing new features that could enhance user experience and make the app fun to use.
Companies undeniably need to have a cross-platform mobile strategy to be resilient in the face of unprecedented innovation. They require a sustainable way to build apps that keep up with the proliferation of new devices and capabilities. They also need efficient ways to support and maintain apps and they need to be more agile and deliver business value faster.
Xamarin has reached 2.6 billion devices with existing teams and code
Xamarin provides a straightforward path for bringing existing C# skills, teams, tools, and code to the world’s most popular mobile platforms. Xamarin has gained traction with over 1 million unique developer downloads and 15,000 customers. In the past 12 months, Xamarin’s developer community has grown 98 percent and sales have more than doubled. Xamarin’s differentiation stems from its ability to build native and hybrid apps for iOS, Android, Mac and Windows using a single C# code base.
And needless to say that among all the cross platforms, the one which has been standing out is Xamarin.Forms.
So what exactly is Xamarin.Forms?
Xamarin.Forms is a cross-platform natively backed UI toolkit abstraction that allows developers to easily create user interfaces that can be shared across Android, iOS, and Windows Phone. The user interfaces are rendered using the native controls of the target platform, allowing Xamarin.Forms applications to retain the appropriate look and feel for each platform.
Xamarin.Forms provides a single API for creating user interfaces with controls and layouts. At runtime, Xamarin.Forms control will be mapped to the appropriate native control and that is what will be rendered.
There are four main classes that are used to compose Xamarin.Forms apps:
• View – these are typically referred to as controls or widgets in other platforms. They correspond to UI elements such as labels, buttons, text fields, etc.

• Page – a Xamarin.Forms represents a single screen in your application. These are analogous to an Android Activity, a Windows Phone Page, or an iOS View Controller.
• Layout – this is a specialized View subtype. It is meant to act as a container for other Layout or Views. Layout subtypes typically contain logic that is specific to organizing the child views in a certain way.
• Cell – This class is a specialized element that is used for items in a list or a table. It describes how each item in a list should be drawn.
Advantages of Xamarin.Forms mobile platform:
1.Rapid Prototyping of Mobile Apps
While creating complex mobile apps, developers often have to spend a lot of time and effort on prototyping. Along with being written in C#, Xamarin Forms applications are native. So these applications can take advantages other APIs and features of the underlying mobile platform.
2. Option to Decide User Interface Development Technique
Xamarin.Forms further allows developers to create user interfaces in two distinct ways. The programmers can avail the API provided by the framework to create user interface views completely with source code.
3. Several Pages
While creating Xamarin.Forms applications, the developers have option to use several pages. The pages can be defined as the application’s screens. Based on the mobile platform, a page can be a View Controller in iOS, an activity in Android, or a Page in Windows Phone. The developers can customize the user interface’s look and feel by using several types of pages including content page, navigation page, tabbed page, carousel page, or master detail page.
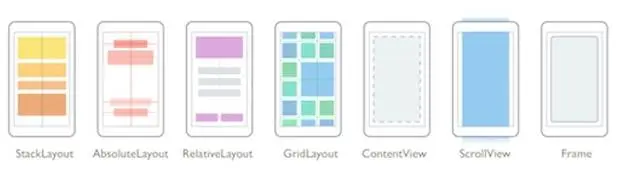
4. Variety of Layouts
Like pages, Xamarin Forms allows developers to use a variety of layouts. They can further use the layout as a container for both views and other containers. Based on the requirements of the application, the programmers can use stack, absolute, relative, or grid layout.
5. 40-plus Controls
The developers can make also of over 40 views as user interface elements. Typically, the end-users will interact with these controls. They can make use of Entry as a single-line form element to receive user input, Button to begin a user command, Image to display images to the user, and Listview to display information in cells.
WinWire expertise in building cross-platform mobile applications
Being experts at building cross-platform mobile applications for all major platforms – iOS, Android and Windows, our developers at WinWire Technologies believe that today the entirely new approach is the way to go and that is – using Xamarin development environment and C#.
Note: In case, you wish to gain more insight into Xamarin.Forms platform, watch thison-demandwebinar here.


